728x90
# Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm
- Max-Flow 문제를 해결할 수 있는 대표적인 알고리즘이다.
- 주어진 그래프 G와 현재 Flow f로 정의되는 잔여 그래프(residual graph) Gf를 이용해서 해결된다.
# Residual graph 초기화
- G의 vertex와 edge를 모두 G0로 copy한다.
- G0의 edge 중 one-way-path edge를 edge(v,u)를 G0에 추가한다. 이때 edge(v,u)의 capacity는 0으로 정의한다.
- one-way-path : edge(u,v)는 있으나 edge(v,u)는 없는 경우
- 2번의 작업상태에 있는 그래프를 G'이라고 칭할 예정이다.
#Augumenting path : 증가 경로
- G'의 source 에서 sink 까지 가는 path 중에 모든 edge의 capacity가 positive( 0 미포함)인 path.
- flow f>=0에 대하여 residual graph Gf 에서 augumenting path가 존재하지 않을 때 까지 그래프의 edge 값을 업데이트 하며 진행한다.
- augumenting path는 unique하지 않다.
- source : indegree가 0인 vertex
- sink : outdegree가 0인 vertex
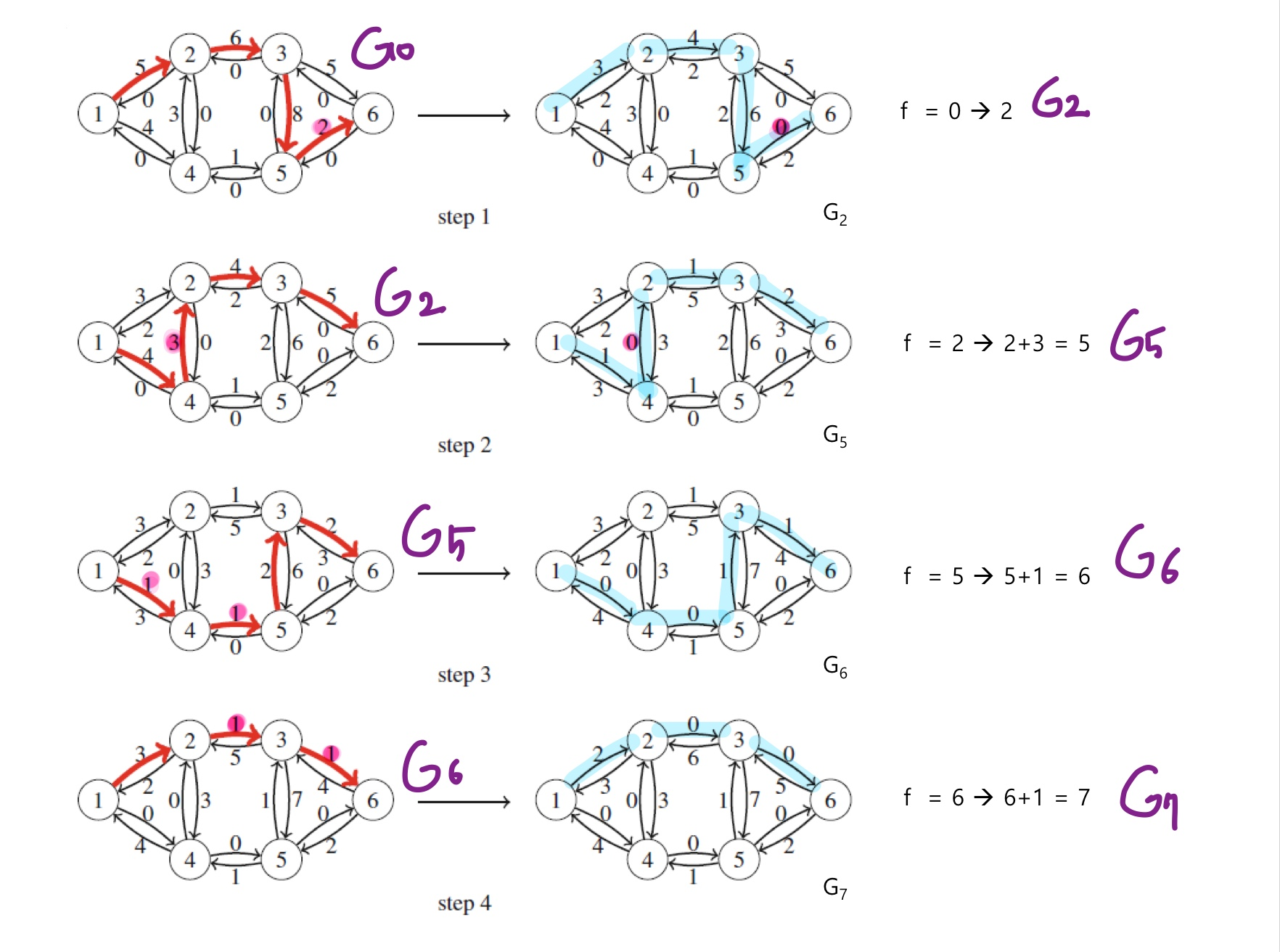
# 진행 과정
- Gf에서 augumenting path를 아무거나 하나 지정한다.
- 해당 Path를 이루는 edge들 중 capacity 최소값을 f'이라고 한다.
- 지정한 augumenting path를 이루는 모든 edge(u,v)의 capacity에 f'을 뺀다.
- edge(u,v)∈Path P : c(u,v) -f'
- 반대쪽 direct edge(v,u)의 capacity에 f'을 더한 후 다시 augumenting edge를 탐색한다.
- edge(v,u) : c(u,v) + f'
- searching augumenting path
- flow를 flow+f'으로 update한다.
더이상 augument pathing을 찾을 수 없을 때 저장되어있는 flow가 max-flow가 된다.
#증명
https://gazelle-and-cs.tistory.com/60
# 코드
참고 : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ford-fulkerson-algorithm-for-maximum-flow-problem/
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
//그래프의 vertex 수
#define V 6
// sorce 에서 sink로 가는 path가 존재한다면 true를 반환한다.
// 해당 경로를 parent array에 저장한다.
bool bfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, int t, int parent[])
{
bool visited[V]; // 방문한 vertex를 저장하기 위한 배열 선언
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited)); // 모든 vertex를 방문하지 않았음으로 초기화
queue<int> q;
q.push(s); // source부터 탐색 시작.
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1; // source가 시작 노드임을 명시
// Standard BFS Loop
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (visited[v] == false && rGraph[u][v] > 0) {
// sink에 도달할 수 있는 경로가 존재하고. BFS를 더 이상 탐색할 수 없을 경우
// parent를 지정 한 후 true를 반환하여 BFS가 종료되었음을 알린다
if (v == t) {
parent[v] = u;
return true;
}
q.push(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// sink에 도달하지 못했을 경우 flase를 반환한다.
return false;
}
// residual graph에서 s to t의 edge 중 최소 capacity를 찾는다
int fordFulkerson(int graph[V][V], int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
int rGraph[V][V];
// Residual graph where rGraph[i][j]
// indicates residual capacity of edge
// from i to j (if there is an edge. If rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is not)
// positiva integr만을 탐색
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
int parent[V]; // This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
// Augment the flow while there is path from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent)) {
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along
// the path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the
// maximum flow through the path found.
int path_flow = INT_MAX;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
// Return the overall flow
return max_flow;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[V][V]
= { { 0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0 }, { 0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
cout << "The maximum possible flow is "
<< fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5);
return 0;
}
#시간복잡도
- G의 capacit가 모두 non-negative integer인 경우 G의 maximum flow를 f라고 하면 각 step마다 augumenting path를 찾기 위해 bfs의 시간 복잡도와 같은 O(m+n) = O(m) 만큼의 시간이 소모된다.
- Ford-Fulkerson Algorithmdml 시간 복잡도는 O(mf)가 된다.
- G0 -> ... -> Gf에 도달하여 종료한다.
- 이는 다음 step으로 넘어갈 때 적어도 1의 flow는 증가함을 보인다.
- 최악의 경우라도 maxinum flow 값 보다 많이 step을 진행하지 않는다.
Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm은 capacity가 큰 edge가 있는 경우 비효율 적이다.
이를 해결하기 위한 graph == Edmonds-Karp algorithm
# Edmonds-Karp algorithm
- augumenting path를 고를 때 edge의 개수가 최소인 path(unweighted shortest path)를 고를 경우 최대 O(mn)번의 upate만 진행한다는 사실이 증명되어있다.
- maximum flow와 무관하게 / m: edge개수 / n : vertex 개수
- augumenting path를 찾을 때 DFS가 아니라 BFS를 사용하면 O(nm^2)시간에 maximum flow를 찾을 수 있다.
- 위의 코드는 BFS를 사용하였기에 Edmonds-Karp algorithm라고 할 수 있지만 adjacency matrix를 사용하였으므로 실제 수행시간은 O(n^3m)이다.
- adjacency list로 구현했을 경우 O(nm^2)의 시간복잡도를 갖게 된다.

728x90
'🐣 알고리즘 삐약 > ✌️알고리즘 개념 잡기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Range Queries] Segment Tree | C++ (0) | 2022.05.17 |
|---|---|
| [Network Flow Applications] Min Cut Problem (0) | 2022.05.09 |
| [Network Flow] 네트워크 플로우 (0) | 2022.05.06 |
| [DP] Dynamic Programing (0) | 2022.04.21 |
| [Problem Solving Paradigms] Greedy (0) | 2022.04.20 |